Fluoroquinolones
Fluoroquinolones are a class of antibiotics that are used to treat bacterial infections. They work by inhibiting the enzymes that are essential for the replication and repair of bacterial DNA. This ultimately leads to the death of the bacteria.
Mechanism of Action
Fluoroquinolones work by inhibiting DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV, two enzymes that are essential for bacterial DNA replication and repair. By targeting these enzymes, fluoroquinolones effectively disrupt the DNA synthesis process, leading to bacterial cell death.
Common Fluoroquinolones
- Ciprofloxacin
- Levofloxacin
- Moxifloxacin
- Norfloxacin
- Ofloxacin
Indications
Fluoroquinolones are used to treat a wide range of bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, and certain sexually transmitted diseases.
Adverse Effects
Common side effects of fluoroquinolones include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and dizziness. More serious but rare side effects may include tendon rupture, nerve damage, and allergic reactions.
Precautions
It is important to use fluoroquinolones with caution, especially in children and adolescents, as they may affect the development of bones, joints, and muscles. Additionally, fluoroquinolones should be used with caution in elderly patients and those with a history of tendon disorders.
Study Guide
- What is the mechanism of action of fluoroquinolones?
- List five common fluoroquinolones.
- What are the common indications for using fluoroquinolones?
- What are the common adverse effects of fluoroquinolones?
- Why should fluoroquinolones be used with caution in certain patient populations?
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Earthquakes

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson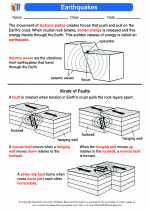
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
