Groundwater
Groundwater is the water that is found beneath the earth's surface in the spaces between soil particles and rocks. It is stored in and moves slowly through geologic formations called aquifers. Groundwater is a vital natural resource as it provides drinking water for many people and supports ecosystems by sustaining streams, rivers, and wetlands.
How Groundwater is Formed
Groundwater is formed when rain and snowmelt seep into the ground and percolate through the soil and rock. The water fills the spaces between particles and forms aquifers. Aquifers can range in size from small, localized bodies of water to vast underground reservoirs.
Importance of Groundwater
Groundwater is important for many reasons. It serves as a source of drinking water for communities around the world. It also supports agriculture by providing water for irrigation. Furthermore, groundwater plays a crucial role in maintaining the flow of streams and rivers, especially during dry periods when surface water is scarce.
Study Guide
- Define groundwater and explain where it is found.
- Describe how groundwater is formed.
- Discuss the importance of groundwater for human activities and ecosystems.
- Explain the concept of aquifers and their role in storing and transporting groundwater.
- Identify the potential threats to groundwater quality and ways to protect this important resource.
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Earthquakes

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson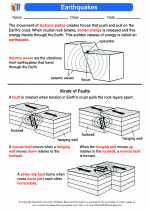
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
