Introduction to "Homo"
"Homo" is a genus of primates that emerged around 2.8 million years ago. The members of this genus are known for their advanced cognitive abilities, tool-making skills, and capacity for complex social interactions. The genus "Homo" includes several extinct species as well as modern humans, Homo sapiens.
Key Species in the Genus "Homo"
- Homo habilis: This species, which lived approximately 2.8 to 1.5 million years ago, is known for its tool-making abilities and is considered one of the earliest members of the genus "Homo."
- Homo erectus: Homo erectus lived from about 2 million to 140,000 years ago and is believed to have been the first hominin to migrate out of Africa.
- Homo neanderthalensis: Neanderthals, who lived in Europe and Asia from approximately 400,000 to 40,000 years ago, are the closest extinct relatives of modern humans.
- Homo sapiens: Modern humans, Homo sapiens, emerged in Africa around 300,000 years ago and are the only surviving species in the genus "Homo."
Notable Characteristics of the Genus "Homo"
- Bipedalism: Members of the genus "Homo" are known for their ability to walk on two legs, a characteristic that distinguishes them from earlier hominin species.
- Encephalization: The genus "Homo" is characterized by an increase in brain size compared to earlier hominin species, indicating a greater capacity for complex thought and behavior.
- Tool Use: Various species within the genus "Homo" are known for their tool-making abilities, reflecting an increasing reliance on technology and cultural adaptation.
- Social Organization: Homo species exhibit evidence of complex social structures and cooperative behavior, as seen in archaeological findings and studies of modern human societies.
Discussion Points for Further Exploration
Consider the following questions for deeper understanding of the genus "Homo":
- How did environmental changes and adaptations influence the evolution of Homo species?
- What evidence supports the hypothesis that Homo sapiens interbred with other Homo species, such as Neanderthals?
- How did the emergence of Homo sapiens contribute to the extinction of other Homo species?
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Earthquakes
Study Guide Earthquakes
Earthquakes  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson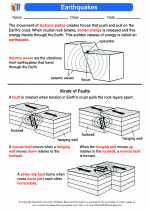 Earthquakes
Earthquakes  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Earthquakes
Earthquakes  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Earthquakes
Earthquakes  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Earthquakes
Earthquakes  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Earthquakes
Earthquakes  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Earthquakes
Earthquakes  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Earthquakes
Earthquakes  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Earthquakes
Earthquakes  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Earthquakes
Earthquakes  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Earthquakes
Earthquakes  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Earthquakes
Earthquakes  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Earthquakes
Earthquakes  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Earthquakes
Earthquakes 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
