Earthquakes -> time
Time
Time is a fundamental concept in the field of science. It is a measure of the duration of events and the intervals between them. In physics, time is considered a fourth dimension along with the three dimensions of space. It is a critical component in understanding the motion of objects, the occurrence of events, and the functioning of natural processes.
Units of Time
In the International System of Units (SI), the base unit of time is the second (s). Other commonly used units of time include minutes (min), hours (hr), days (d), and years (yr).
Measuring Time
Time can be measured using various instruments such as clocks, watches, and electronic devices. The most accurate timekeeping is done using atomic clocks, which are based on the vibrations of atoms.
Time Zones
Due to the Earth's rotation, different parts of the world experience time at different intervals. This has led to the establishment of time zones, each representing a region where the local time is the same.
Study Guide
- Define time and explain its significance in the field of science.
- List and describe the units of time used in the International System of Units (SI).
- How is time measured and what are the most accurate timekeeping devices?
- Explain the concept of time zones and their relevance in global timekeeping.
- Discuss the relationship between time and the motion of objects.
- Research the history of timekeeping and the evolution of time measurement devices.
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Seventh Grade. Earthquakes

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson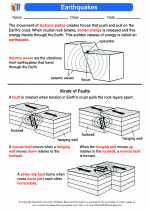
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
