Big Bang Theory
The Big Bang Theory is the prevailing cosmological model for the observable universe from the earliest known periods through its subsequent large-scale evolution. It describes how the universe expanded from a very high-density and high-temperature state, and offers a comprehensive explanation for a broad range of phenomena, including the abundance of light elements, the cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation, and large-scale structure.
Key Concepts to Understand:
- Origin of the Universe: The Big Bang Theory proposes that the universe began as a singularity - a point of infinite density and temperature - and then rapidly expanded.
- Expansion of the Universe: The universe continues to expand, with galaxies moving away from each other, as evidenced by the redshift of light from distant galaxies.
- Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) Radiation: The CMB is the afterglow of the Big Bang and provides strong evidence for the early hot and dense state of the universe.
- Formation of Elements: The Big Bang Theory explains the synthesis of light elements such as hydrogen, helium, and lithium during the early stages of the universe.
- Observable Universe: The Big Bang Theory provides a framework for understanding the observable universe and its large-scale structure, including the formation of galaxies and galaxy clusters.
Study Tips:
- Understanding the Timeline: Familiarize yourself with the timeline of the universe as proposed by the Big Bang Theory, including the early stages of expansion and the formation of different elements.
- Key Evidence: Pay attention to the key pieces of evidence that support the Big Bang Theory, such as the cosmic microwave background radiation and the redshift of galaxies.
- Compare with Alternative Models: Compare the Big Bang Theory with alternative models of the universe's origin and expansion, such as the steady-state theory, to understand the strengths and weaknesses of each.
- Stay Updated: Keep up with current research and developments in cosmology to see how the Big Bang Theory continues to be tested and refined.
Practice Questions:
- What is the Big Bang Theory, and how does it explain the origin of the universe?
- What is the cosmic microwave background radiation, and why is it considered a crucial piece of evidence for the Big Bang Theory?
- Describe the process of element formation as proposed by the Big Bang Theory.
- How does the expansion of the universe support the Big Bang Theory?
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Eighth Grade. Circulation and immunity
Study Guide Circulation and immunity
Circulation and immunity  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key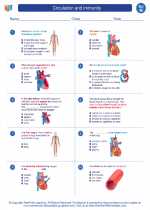 Circulation and immunity
Circulation and immunity  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key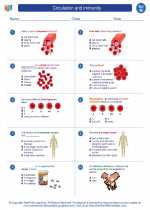 Circulation and immunity
Circulation and immunity  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key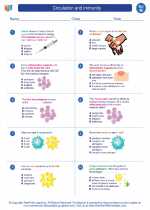 Circulation and immunity
Circulation and immunity  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Circulation and immunity
Circulation and immunity  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Circulation and immunity
Circulation and immunity  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Circulation and immunity
Circulation and immunity  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Circulation and immunity
Circulation and immunity  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Circulation and immunity
Circulation and immunity  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Circulation and immunity
Circulation and immunity  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Circulation and immunity
Circulation and immunity 

 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
