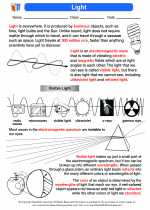
Geometric Optics
Geometric optics is a branch of optics that deals with the behavior of light as it travels through different media and interacts with optical elements such as lenses and mirrors. This branch of physics focuses on understanding the principles governing the propagation of light and the formation of images. The study of geometric optics is crucial in various fields such as astronomy, photography, and ophthalmology.
Key Concepts in Geometric Optics
- Reflection: The bouncing back of light when it strikes the surface of an object. This can occur on smooth surfaces such as mirrors, leading to the formation of images.
- Refraction: The bending of light as it passes from one medium to another of different optical density. This phenomenon is responsible for the way lenses and prisms manipulate light.
- Lenses: Transparent optical elements that refract light to form images. There are two main types of lenses: convex (converging) lenses and concave (diverging) lenses.
- Mirrors: Surfaces with high reflectivity that can produce images through reflection. There are two types of mirrors: concave mirrors and convex mirrors.
- Image Formation: Understanding how light rays interact with optical elements to produce real or virtual images, and determining the properties of these images.
Study Guide for Geometric Optics
To effectively understand geometric optics, it is essential to grasp the following key topics:
- Light Propagation: Learn about the behavior of light rays as they travel through different media and interact with optical elements.
- Reflection and Mirrors: Understand the laws of reflection and how images are formed by concave and convex mirrors.
- Refraction and Lenses: Master the principles of refraction and the behavior of light passing through convex and concave lenses.
- Ray Diagrams: Practice drawing and interpreting ray diagrams to understand image formation by mirrors and lenses.
- Image Properties: Familiarize yourself with the characteristics of images formed by mirrors and lenses, including size, orientation, and type (real or virtual).
By comprehensively studying these concepts and practicing with relevant problems and examples, you can gain a solid understanding of geometric optics and its applications in various fields.
.