Mirrors
Mirrors are surfaces that reflect light and form images. They are widely used in everyday life, in various applications such as personal grooming, interior decoration, scientific instruments, and optical devices. There are different types of mirrors, each with unique properties and applications. Understanding the principles of reflection and the behavior of light when it interacts with mirrors is essential for grasping the concept of mirrors.
Types of Mirrors
There are two primary types of mirrors: concave and convex mirrors.
Concave Mirrors
Concave mirrors are curved inward and have reflective surfaces on the inner side. They are capable of forming both real and virtual images, depending on the object's position relative to the mirror. These mirrors are commonly used in applications such as reflecting telescopes, makeup mirrors, and headlights.
Convex Mirrors
Convex mirrors are curved outward and have reflective surfaces on the outer side. They always form virtual images, regardless of the object's position. These mirrors are used in applications such as security mirrors, side-view mirrors for vehicles, and magnifying glasses.
Principles of Reflection
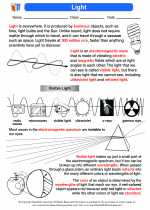
When light strikes a mirror, it undergoes reflection, where it bounces off the surface of the mirror. The angle of incidence (the angle at which the light strikes the mirror) is equal to the angle of reflection (the angle at which the light reflects off the mirror). This principle is known as the law of reflection.
Study Guide
Here are some key points to study when learning about mirrors:
- Types of mirrors: Understand the differences between concave and convex mirrors, along with their respective properties and applications.
- Reflection principles: Learn about the law of reflection and how it governs the behavior of light when it interacts with mirrors.
- Image formation: Study how mirrors form images, including the characteristics of the images produced by concave and convex mirrors.
- Ray diagrams: Practice drawing ray diagrams to understand how light rays behave when reflected by concave and convex mirrors.
- Applications: Explore the various real-world applications of mirrors and how their unique properties are utilized in different fields.
By mastering these concepts, you will develop a comprehensive understanding of mirrors and their role in optics and everyday life.