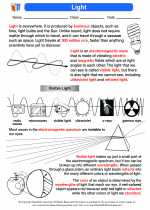
Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics is the branch of physics that deals with the behavior of particles at the atomic and subatomic levels. It provides a mathematical description of the wave-particle duality of energy and matter and the probabilistic nature of their interactions.
Here is a study guide to help you understand the key concepts of quantum mechanics:
- Wave-particle duality: Explain the concept of particles and energy exhibiting both wave-like and particle-like properties. Discuss the famous double-slit experiment that demonstrated this duality.
- Quantization of energy: Describe how energy levels in atoms and molecules are quantized, leading to the understanding of discrete energy states and the emission and absorption of photons.
- Heisenberg's uncertainty principle: Explain how this principle states that the more precisely the position of a particle is known, the less precisely its momentum can be known, and vice versa.
- Wave functions and probability: Discuss how the wave function represents the probability amplitude of a particle's position and how it is used to calculate the probability of finding a particle in a particular region of space.
- Quantum superposition: Explain the concept of superposition, where particles can exist in multiple states simultaneously, and how this forms the basis of quantum computing and cryptography.
- Quantum entanglement: Describe the phenomenon where the quantum states of two or more particles become linked in such a way that the state of one particle cannot be described independently of the state of the others.
Understanding these concepts is crucial for grasping the fundamental principles of quantum mechanics and its applications in various fields of science and technology.
.