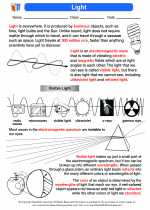
Thermoregulation
Thermoregulation is the process that allows the human body to maintain its core internal temperature within a narrow, optimal range, despite changes in the external environment.
Key Concepts
- Homeostasis: The body's ability to maintain a stable internal environment, including temperature, through various physiological mechanisms.
- Temperature Regulation: The processes involved in maintaining a constant body temperature, including heat production, conservation, and dissipation.
- Heat Production: The body generates heat through metabolic processes, such as cellular respiration and muscle activity.
- Heat Conservation: Mechanisms like vasoconstriction, shivering, and insulation help retain heat in the body.
- Heat Dissipation: Processes like vasodilation, sweating, and respiration enable the release of excess heat from the body.
- Thermoreceptors: Specialized nerve cells that detect changes in temperature and relay this information to the brain for appropriate responses.
Mechanisms of Thermoregulation
The human body employs several mechanisms to regulate its temperature:
- Behavioral Responses: Actions such as seeking shade, wearing appropriate clothing, and adjusting environmental conditions to maintain a comfortable temperature.
- Physiological Responses: Involuntary processes like sweating, shivering, and changes in blood flow to adjust heat exchange with the environment.
- Endocrine Regulation: Hormones like adrenaline and thyroxine play a role in controlling metabolic rate and heat production.
Factors Affecting Thermoregulation
Various factors can influence the body's ability to regulate temperature:
- External Environment: Ambient temperature, humidity, and airflow impact the body's heat exchange with the surroundings.
- Physical Activity: Exercise and movement increase heat production and may require enhanced cooling mechanisms.
- Illness and Injury: Fever, infections, and damage to thermoregulatory centers in the brain can disrupt temperature control.
- Age and Gender: Children, elderly individuals, and pregnant women may have different thermoregulatory responses due to developmental or hormonal factors.
Study Tips
When studying thermoregulation, it's important to focus on understanding the various mechanisms involved in maintaining body temperature and the factors that can impact these processes. Here are some tips to help you prepare for your science exam:
- Review the different ways the body can generate and lose heat.
- Understand the roles of thermoreceptors and the brain in coordinating temperature regulation.
- Learn about specific physiological responses to heat and cold, such as sweating, shivering, and vasoconstriction/dilation.
- Consider real-life scenarios and how the body adapts to different environmental conditions or physical activities.
- Practice applying your knowledge to case studies or problem-solving questions related to thermoregulation.
By mastering these concepts and applying them to practical situations, you'll be well-prepared to demonstrate your understanding of thermoregulation.
.