Light -> wavelength
Wavelength: Explanation and Study Guide
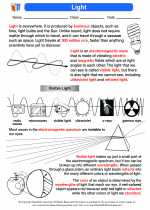
Wavelength is a fundamental concept in the study of waves, including electromagnetic waves and sound waves. It is defined as the distance between two consecutive points of a wave that are in phase, such as the distance between two consecutive peaks or troughs.
Key Points to Understand about Wavelength:
- Wavelength is represented by the Greek letter lambda (λ).
- It is measured in units of length, such as meters (m) or nanometers (nm).
- For electromagnetic waves, shorter wavelengths correspond to higher frequencies, while longer wavelengths correspond to lower frequencies.
- In the case of sound waves, shorter wavelengths correspond to higher pitches, while longer wavelengths correspond to lower pitches.
- The relationship between wavelength, frequency, and wave speed is given by the formula:
wavelength = wave speed / frequency
Study Guide:
To understand wavelength thoroughly, it's important to grasp the following concepts:
- Wave Properties: Understand the properties of waves, including amplitude, frequency, and wavelength.
- Wave Types: Differentiate between electromagnetic waves and mechanical waves, such as sound waves, and how wavelength applies to each type.
- Wavelength Calculations: Be able to solve problems and calculate wavelength using the formula:
wavelength = wave speed / frequency - Frequency-Wavelength Relationship: Understand how the frequency of a wave relates to its wavelength and vice versa.
- Real-world Applications: Explore real-world examples of wavelength, such as in radio waves, visible light, and musical notes.
By mastering these key points and studying the associated concepts, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of wavelength and its relevance to the study of waves.