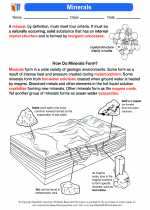
Biomass
Biomass is a renewable energy source that is derived from organic materials such as plants, wood, agricultural residues, and waste. It is a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels for the generation of heat, electricity, and biofuels.
Types of Biomass
- Woody Biomass: This includes trees, branches, and wood chips, which can be used for heating and electricity generation.
- Agricultural Biomass: This comprises of crop residues, such as corn stover, wheat straw, and rice husks, that can be used for energy production.
- Animal Waste: Organic waste from livestock, such as manure, can be converted into biogas and used as a source of renewable energy.
- Urban Solid Waste: Municipal solid waste, including paper, cardboard, and food waste, can be processed and utilized for energy generation.
Conversion Processes
Biomass can be converted into energy through various processes, including:
- Combustion: Burning biomass directly to produce heat or electricity.
- Gasification: Converting biomass into a gas mixture, which can be used for power generation or the production of biofuels.
- Anaerobic Digestion: Decomposing organic materials to produce biogas, which can be used for heating or electricity.
- Biochemical Conversion: Using microorganisms to ferment biomass and produce biofuels, such as ethanol and biodiesel.
Environmental Benefits
Utilizing biomass for energy offers several environmental advantages, including:
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels.
- Support for sustainable land management and waste reduction.
- Potential for carbon neutrality when using organic waste materials.
Challenges and Considerations
While biomass has many benefits, there are also challenges and considerations to be aware of, such as:
- Competition with food production and land use.
- Efficient collection and transportation of biomass materials.
- Impact on local air quality and emissions from biomass combustion.
Study Guide
Here are some key points to focus on when studying biomass:
- Define biomass and its significance as a renewable energy source.
- Identify different types of biomass and their potential applications.
- Explain the various conversion processes for biomass energy production.
- Discuss the environmental benefits and challenges associated with biomass utilization.
- Compare and contrast biomass with other renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power.
Understanding biomass is important for addressing global energy needs and mitigating climate change. By mastering this topic, you will gain insight into the potential of biomass as a sustainable energy solution.
.