Magma: Definition and Characteristics
Magma is a molten or semi-molten rock material found beneath the Earth's surface. It is generated by the partial melting of the Earth's crust or mantle. Magma can vary in composition, temperature, and viscosity, leading to the formation of different types of igneous rocks when it solidifies.
Types of Magma
- Basaltic Magma: This type of magma has a low silica content and is relatively fluid. It often leads to the formation of basaltic rocks, such as basalt and gabbro.
- Andesitic Magma: Andesitic magma has a higher silica content and intermediate viscosity. It can give rise to andesite and diorite rocks.
- Rhyolitic Magma: Rhyolitic magma is high in silica and has high viscosity. It is associated with the formation of rhyolite and granite rocks.
Formation and Movement of Magma
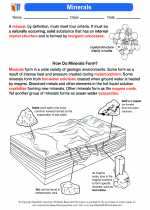
Magma is formed through the process of partial melting within the Earth's crust or mantle. It can move upwards towards the surface through cracks and fractures in the rock, a process known as magma migration. When magma reaches the surface, it erupts as lava through volcanic activity.
Effects of Magma
Magma plays a crucial role in the formation of igneous rocks, which are an essential part of the Earth's crust. It also contributes to the creation of volcanic landforms, such as volcanoes, calderas, and lava plateaus. Additionally, the heat from magma can drive geothermal energy production and influence tectonic activity.
Study Guide
When studying magma, it's important to focus on the following key points:
- Understanding the composition and characteristics of different types of magma.
- Exploring the processes involved in the formation of magma and its movement within the Earth.
- Recognizing the impact of magma on the formation of igneous rocks and volcanic landforms.
- Examining the role of magma in geological processes and its significance in Earth's dynamics.
By mastering these concepts, you'll have a solid understanding of the role of magma in shaping the Earth's geology and its broader implications for natural processes and human activities.
.