Circadian Rhythm
A circadian rhythm is a natural, internal process that regulates the sleep-wake cycle and repeats roughly every 24 hours. It is also known as the body's internal clock. This rhythm is influenced by external cues such as light and temperature, and it plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological and behavioral processes.
Key Concepts
- Internal Clock: The circadian rhythm is controlled by a group of cells in the brain called the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), which responds to light and dark signals received from the eyes.
- Sleep-Wake Cycle: The circadian rhythm helps regulate the timing of sleep and wakefulness, influencing patterns of alertness, body temperature, hormone production, and other bodily functions.
- External Influences: Environmental factors such as light exposure, meal times, and social activities can affect the circadian rhythm, leading to disruptions in the sleep-wake cycle.
Study Tips
When studying circadian rhythm, it's important to understand the following key points:
- Describe the role of the suprachiasmatic nucleus in regulating the circadian rhythm.
- Explain how light exposure affects the body's internal clock and impacts the sleep-wake cycle.
- Discuss the potential consequences of disrupting the circadian rhythm, including sleep disorders and health implications.
- Analyze the significance of maintaining a regular sleep schedule and healthy sleep habits for overall well-being.
Sample Questions
- What is the primary role of the suprachiasmatic nucleus in the circadian rhythm?
- How does exposure to light influence the body's internal clock and affect sleep patterns?
- What are the potential consequences of irregular sleep-wake cycles on an individual's health and behavior?
- Why is it important to maintain a consistent sleep schedule and practice healthy sleep habits?
By understanding the concepts and implications of circadian rhythm, you will gain insights into the vital role of our body's internal clock in maintaining overall well-being and optimal functioning.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Eighth Grade. Plate tectonics
Study Guide Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson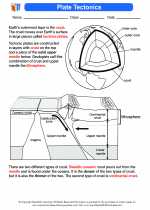 Plate Tectonics
Plate Tectonics  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
