What is Dark Energy?
Dark energy is a hypothetical form of energy that permeates all of space and exerts a negative pressure, causing the expansion of the universe to accelerate. It is thought to make up about 68% of the total mass-energy content of the universe.
Discovery and Evidence
The existence of dark energy was first suggested in the late 1990s, based on observations of distant supernovae. These observations showed that the universe's expansion was not slowing down as expected, but rather accelerating. This led to the idea that some unknown force, later dubbed "dark energy," was counteracting the force of gravity and driving the acceleration.
Properties of Dark Energy
Dark energy is believed to have the following properties:
- Negative Pressure: Dark energy is associated with a negative pressure, which is thought to be responsible for the repulsive gravitational effect causing the universe's expansion to accelerate.
- Uniformity: Dark energy is considered to be homogeneously distributed throughout space, leading to its pervasive influence on the large-scale structure of the universe.
- Constant Energy Density: Some theories propose that dark energy has a constant energy density, while others suggest that it may vary over time.
Role in the Universe
Dark energy's dominant role in the universe's energy budget has significant implications for the future of the cosmos. If its influence continues to drive the universe's expansion, it may ultimately lead to the "Big Rip," a hypothetical scenario in which the accelerating expansion becomes so powerful that it tears apart galaxies, stars, and even fundamental particles.
Study Guide
Here are some key points to focus on when studying dark energy:
- Understand the concept of dark energy and its role in the universe's expansion.
- Explore the observational evidence that led to the discovery of dark energy, including the use of Type Ia supernovae as standard candles.
- Examine the properties and possible origins of dark energy, such as the cosmological constant and dynamical field theories.
- Consider the implications of dark energy for the ultimate fate of the universe.
- Compare and contrast dark energy with dark matter and ordinary matter, understanding their distinct roles in the universe.
By mastering these concepts and exploring the latest research in cosmology, you can gain a deeper understanding of dark energy and its profound implications for our understanding of the cosmos.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Eighth Grade. Plate tectonics

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson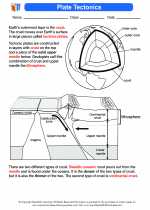
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
