Feedback Mechanisms
Feedback mechanisms are processes that help regulate the body's internal environment. They maintain stability and allow the body to respond to changes in the environment. There are two main types of feedback mechanisms: negative feedback and positive feedback.
Negative Feedback
Negative feedback is the most common type of feedback mechanism in the body. It operates to maintain homeostasis by counteracting any deviation from the set point. When a change occurs, negative feedback works to bring the system back to its normal functioning level.
- Example: Regulation of body temperature. When the body temperature rises, the body sweats to lower the temperature. When the body temperature falls, shivering occurs to generate heat and raise the temperature.
Positive Feedback
Positive feedback mechanisms amplify or reinforce changes. Unlike negative feedback, positive feedback moves the system further away from the original set point. It is less common in biological systems and is typically associated with processes that need to be rapidly completed.
- Example: Blood clotting. When an injury occurs, platelets release chemicals that attract more platelets to the site, forming a clot. This process continues until the clot is big enough to stop the bleeding.
Study Guide
To better understand feedback mechanisms, make sure to focus on the following key points:
- Define feedback mechanisms and their purpose in the body.
- Identify the differences between negative and positive feedback mechanisms.
- Give examples of negative and positive feedback mechanisms in the human body.
- Explain the role of feedback mechanisms in maintaining homeostasis.
- Discuss the importance of feedback mechanisms in response to environmental changes.
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Eighth Grade. Plate tectonics

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson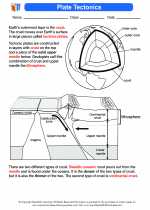
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
