Glaciers
A glacier is a large mass of ice that moves slowly over land. They are formed from accumulated snow that has compacted into ice over many years. Glaciers are a key indicator of climate change and have a significant impact on the Earth's landscape.
Formation of Glaciers
Glaciers form in areas where the accumulation of snow exceeds its melting and sublimation over many years. As the snow accumulates, it compresses into ice and forms a glacier. This process is known as glaciation.
Types of Glaciers
There are two main types of glaciers: alpine glaciers and ice sheets. Alpine glaciers form in mountainous regions and move downslope through valleys, while ice sheets are large, continental-scale glaciers that cover vast areas of land.
Effects of Glaciers
Glaciers have a significant impact on the Earth's landscape. They can carve out valleys, create fjords, and deposit large amounts of sediments as they move. As glaciers melt, they contribute to rising sea levels and can affect global climate patterns.
Study Guide
- What is a glacier and how is it formed?
- What are the two main types of glaciers?
- What are some of the effects of glaciers on the Earth's landscape?
- How do glaciers contribute to rising sea levels?
- What role do glaciers play in climate change?
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Eighth Grade. Plate tectonics

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson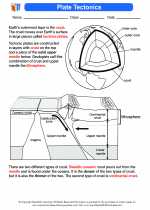
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
