Infectious Agents
An infectious agent, also known as a pathogen, is a biological agent that causes disease or illness to its host.
Types of Infectious Agents
- Bacteria: single-celled microorganisms that can cause a wide range of diseases such as strep throat, tuberculosis, and urinary tract infections.
- Viruses: tiny infectious agents that can only replicate inside the cells of a living organism, causing illnesses like the flu, HIV/AIDS, and COVID-19.
- Fungi: organisms such as molds and yeasts that can cause infections like athlete's foot, ringworm, and thrush.
- Parasites: organisms that live on or inside a host organism and cause harm, including protozoa, helminths, and ectoparasites like ticks and lice.
Transmission of Infectious Agents
Infectious agents can be transmitted through various means, including:
- Direct contact with infected individuals or their bodily fluids
- Indirect contact with contaminated surfaces or objects
- Airborne transmission through respiratory droplets or aerosols
- Vector-borne transmission via insects or other animals
Preventing the Spread of Infectious Agents
To prevent the spread of infectious agents, it is important to practice good hygiene, such as:
- Regular handwashing with soap and water
- Covering mouth and nose when sneezing or coughing
- Using personal protective equipment when necessary
- Getting vaccinated against infectious diseases
Study Tips
When studying infectious agents, it's important to:
- Understand the differences between bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites.
- Learn about specific diseases caused by different types of infectious agents.
- Be familiar with the modes of transmission for various pathogens.
- Review and understand the importance of preventive measures to control the spread of infectious diseases.
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Eighth Grade. Plate tectonics
Study Guide Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson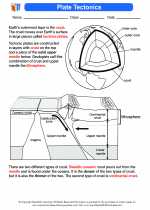 Plate Tectonics
Plate Tectonics  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
