Mitochondria
Mitochondria are double-membrane-bound organelles found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. They are often referred to as the "powerhouse" of the cell because they are responsible for producing the majority of the cell's energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through the process of cellular respiration.
Structure of Mitochondria
The structure of a mitochondrion consists of several key components:
- Outer membrane: The outer membrane of the mitochondria is smooth and contains a large number of integral membrane proteins called porins, which allow the passage of small molecules and ions.
- Inner membrane: The inner membrane is highly folded into structures called cristae, which greatly increase its surface area. This is where the majority of the ATP production takes place. The inner mitochondrial membrane also contains proteins and enzymes involved in cellular respiration.
- Intermembrane space: This is the region between the outer and inner membranes of the mitochondria and plays a role in the transport of molecules and ions.
- Matrix: The matrix is the innermost compartment of the mitochondria and contains enzymes, DNA, ribosomes, and the components necessary for the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) and fatty acid oxidation.
Function of Mitochondria
Mitochondria are involved in several important cellular processes, including:
- ATP Production
- Metabolism
- Calcium Homeostasis
- Apoptosis
Study Guide
To understand mitochondria in depth, it is essential to focus on the following key areas:
- Structure of Mitochondria
- Cellular Respiration
- Metabolism
- Role in Cell Health
Remember to review the functions and structures of mitochondria and their importance in cellular energy production and overall cell function. Understanding the intricate workings of mitochondria will provide a deeper insight into the fundamental processes of life at the cellular level.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Eighth Grade. Plate tectonics

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson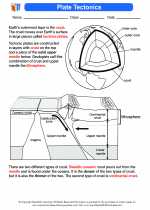
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
