Mouth: Structure and Function
The mouth is the first part of the digestive system, responsible for the intake of food and the initial process of digestion. It is also important for speech and breathing. The mouth is made up of several key structures that work together to carry out these functions.
Key Structures of the Mouth
- Teeth: The mouth contains teeth that are used for biting, chewing, and grinding food into smaller pieces. There are different types of teeth, including incisors, canines, premolars, and molars, each with a specific function in the chewing process.
- Tongue: The tongue is a muscular organ that helps in mixing food with saliva and pushing the food towards the back of the mouth for swallowing. It also plays a crucial role in speech and taste sensation.
- Salivary Glands: These glands produce saliva, which helps in the initial breakdown of food and lubrication for swallowing. Saliva also contains enzymes that start the digestion process.
- Palate: The roof of the mouth is divided into two parts - the hard palate in the front and the soft palate at the back. The palate assists in the process of chewing and swallowing and also separates the oral and nasal cavities.
- Uvula: This small, fleshy structure hangs from the soft palate and plays a role in preventing food from entering the nasal cavity during swallowing.
Functions of the Mouth
The mouth performs several important functions in the human body:
- Ingestion: The process of taking in food and liquids through the mouth.
- Mastication: The act of chewing and breaking down food into smaller pieces, making it easier to swallow and digest.
- Salivation: The production of saliva, which moistens food and begins the process of chemical digestion.
- Speech: The tongue and other structures in the mouth play a crucial role in forming sounds and words for communication.
- Swallowing: The process of moving food from the mouth to the esophagus, allowing it to enter the digestive system.
Study Guide Questions
- What are the functions of the mouth?
- List and describe the key structures of the mouth.
- How does saliva contribute to the digestion process?
- Explain the role of the tongue in the mouth.
- What are the different types of teeth and their functions?
- Describe the process of swallowing in detail.
[Mouth] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Eighth Grade. Plate tectonics
Study Guide Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson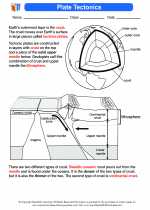 Plate Tectonics
Plate Tectonics  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
