Solid
A solid is one of the fundamental states of matter. It has a definite shape and volume, and its particles are tightly packed together in a regular arrangement.
Properties of Solids
- Definite Shape: Solids have a fixed shape and do not conform to the shape of their container.
- Definite Volume: The volume of a solid remains constant, regardless of the container it is placed in.
- Tightly Packed Particles: The particles in a solid are held together by strong forces of attraction, resulting in a fixed position and a regular arrangement.
- Limited Compressibility: Solids are difficult to compress due to the close arrangement of particles.
- High Density: Solids have a high density due to the close packing of particles.
- Low Fluidity: Solids do not flow and have low fluidity, meaning they maintain their shape under applied forces.
Examples of Solids
Common examples of solids include:
Types of Solids
Solids can be classified into different types based on the arrangement of particles:
- Crystalline Solids: These have a regular, repeating pattern of particles, resulting in a well-defined geometric shape. Examples include salt and sugar.
- Amorphous Solids: These lack a regular, repeating pattern of particles and do not have a well-defined geometric shape. Examples include glass and plastic.
Changes in State
Solids can undergo changes in state under specific conditions:
- Melting: When heat is applied, a solid can change into a liquid through the process of melting.
- Freezing: When heat is removed, a liquid can change into a solid through the process of freezing.
- Sublimation: Some solids can change directly into a gas without passing through the liquid state through the process of sublimation. Dry ice (solid carbon dioxide) is an example of a substance that undergoes sublimation.
Study Guide
Use the following questions to guide your study of solids:
- What are the properties of solids?
- How are crystalline and amorphous solids different?
- Give examples of crystalline and amorphous solids.
- What happens to a solid during the process of melting?
- How does the arrangement of particles in a solid differ from a liquid or gas?
[Solid] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Eighth Grade. Plate tectonics
Study Guide Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson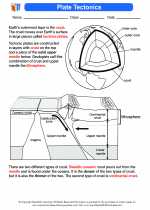 Plate Tectonics
Plate Tectonics  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
