Tectonic Activity
Tectonic activity refers to the movement and interaction of the Earth's lithospheric plates. This movement is responsible for various geological phenomena such as earthquakes, volcanic activity, and the formation of mountain ranges.
Plate Tectonics
Plate tectonics is the scientific theory that describes the large-scale motion of Earth's lithosphere. The lithosphere is divided into several large and small plates that float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere beneath them. The movement of these plates is driven by processes such as mantle convection and ridge push.
Tectonic Boundaries
There are three main types of tectonic boundaries: divergent boundaries, convergent boundaries, and transform boundaries. Divergent boundaries occur where two plates move away from each other, leading to the formation of new crust. Convergent boundaries occur where two plates move towards each other, resulting in subduction zones or mountain building. Transform boundaries occur where two plates slide past each other horizontally.
Geological Events
Tectonic activity leads to various geological events. Earthquakes are caused by the sudden release of energy along faults in the Earth's crust. Volcanic activity occurs when magma from the mantle reaches the Earth's surface, often at convergent or divergent boundaries. The formation of mountain ranges, such as the Himalayas, is also a result of tectonic activity.
Study Guide
Here are some key concepts to understand when studying tectonic activity:
- Plate tectonics and the movement of lithospheric plates
- The three types of tectonic boundaries and their characteristics
- The geological events associated with tectonic activity, including earthquakes, volcanic activity, and mountain formation
- The role of plate movements in shaping the Earth's surface and impacting human activities
It's also important to familiarize yourself with specific examples of tectonic activity, such as the formation of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, the subduction zones in the Pacific Ring of Fire, and the impact of tectonic activity on the distribution of natural resources.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Eighth Grade. Plate tectonics

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson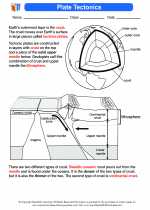
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
