Trace Elements
Trace elements are chemical elements that are required by living organisms in very small quantities. Despite their low abundance, these elements play crucial roles in various biological processes and are essential for the overall health and well-being of organisms. Some of the most important trace elements for living organisms include zinc, copper, iron, selenium, iodine, and manganese.
Importance of Trace Elements
Trace elements serve a variety of functions in the body, including:
- Cofactors for Enzymes: Many trace elements serve as cofactors for enzymes, facilitating various biochemical reactions in the body.
- Structural Role: Some trace elements are essential for the structure and function of specific molecules, such as iron in hemoglobin, which is crucial for oxygen transport in the blood.
- Cellular Signaling: Certain trace elements play a role in cellular signaling and communication within the body.
- Antioxidant Defense: Trace elements like selenium and copper are important components of antioxidant enzymes that help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.
- Hormone Regulation: Iodine, for example, is a key component of thyroid hormones, which are essential for regulating metabolism.
Deficiency and Toxicity
Both deficiency and excess of trace elements can have detrimental effects on the body. Deficiency of certain trace elements can lead to various health problems, such as anemia (iron deficiency), impaired immune function (zinc deficiency), and thyroid disorders (iodine deficiency). On the other hand, excessive intake of certain trace elements can lead to toxicity and negatively impact health.
Sources of Trace Elements
Trace elements can be obtained through diet and supplementation. Foods such as seafood, nuts, seeds, whole grains, and leafy green vegetables are good sources of various trace elements. Additionally, fortified foods and dietary supplements can be used to ensure adequate intake of these essential nutrients.
Study Guide
When studying trace elements, it's important to focus on the following key points:
- Understand the roles of specific trace elements in the body.
- Learn about the sources of trace elements and their absorption in the body.
- Be familiar with the symptoms and health conditions associated with deficiency or excess of specific trace elements.
- Study the recommended dietary allowances (RDAs) for different trace elements and their significance in maintaining health.
- Understand the impact of trace element imbalances on overall health and well-being.
By mastering these concepts, you will gain a thorough understanding of the importance of trace elements in biological systems and their implications for human health.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Eighth Grade. Plate tectonics

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson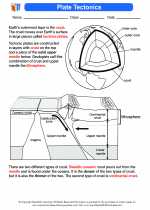
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
