Tropical Rainforests
A tropical rainforest is a type of biome found within the tropical region, characterized by high levels of precipitation and biodiversity. These ecosystems are found in areas near the equator, such as the Amazon Basin in South America, the Congo Basin in Africa, and parts of Southeast Asia.
Climate
Tropical rainforests have a hot and humid climate with little temperature variation throughout the year. They receive high levels of rainfall, typically between 80 to 400 inches annually, creating a lush and dense vegetation cover.
Flora and Fauna
The biodiversity in tropical rainforests is unparalleled, with a wide variety of plant and animal species. The dense canopy of trees, along with the multiple layers of vegetation, provides habitats for countless organisms, including monkeys, birds, snakes, insects, and a vast array of plant species.
Soil and Nutrient Cycling
The soil in tropical rainforests is generally nutrient-poor due to the rapid decomposition of organic matter and the high levels of rainfall, which leach away minerals. However, the ecosystem has developed efficient nutrient cycling processes, with a large portion of nutrients being stored in the biomass of plants and trees.
Threats and Conservation
Tropical rainforests are under threat due to deforestation, primarily for agriculture, logging, and urban development. This has led to the loss of biodiversity and disruption of the delicate ecological balance. Conservation efforts aim to protect these vital ecosystems through measures such as establishing national parks, promoting sustainable land use practices, and supporting indigenous communities.
Study Guide
- Describe the climate of tropical rainforests and its impact on the ecosystem.
- Explain the concept of biodiversity and provide examples of species found in tropical rainforests.
- Discuss the nutrient cycling processes in tropical rainforests and their significance to the ecosystem.
- Analyze the major threats to tropical rainforests and propose conservation strategies to address these threats.
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Eighth Grade. Plate tectonics

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson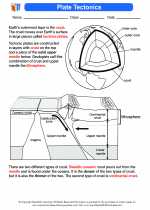
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
