Homozygous
In genetics, the term "homozygous" refers to an organism that has two identical alleles for a particular trait. Alleles are different forms of a gene that can cause different variations of a trait. An organism can be homozygous dominant (having two dominant alleles) or homozygous recessive (having two recessive alleles).
Types of Homozygous:
- Homozygous Dominant (BB): This means that both alleles for a particular gene are the dominant form. For example, if the gene for seed shape in pea plants is denoted by "B" for round seeds (dominant) and "b" for wrinkled seeds (recessive), a pea plant with the genotype "BB" would be homozygous dominant for seed shape.
- Homozygous Recessive (bb): This means that both alleles for a particular gene are the recessive form. Using the same example, a pea plant with the genotype "bb" would be homozygous recessive for seed shape.
Study Guide:
When studying homozygous traits, it's important to understand the concept of alleles and how they determine specific traits in organisms. Here are some key points to focus on when learning about homozygous traits:
- Understand the difference between dominant and recessive alleles.
- Learn how to determine the genotype of an organism based on its phenotype.
- Practice Punnett squares to predict the outcomes of genetic crosses involving homozygous parents.
- Explore real-life examples of homozygous traits in different organisms, such as coat color in cats or eye color in humans.
By mastering the concept of homozygous traits, you can gain a deeper understanding of how genetic inheritance works and how traits are passed down from one generation to the next.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Eighth Grade. Respiration and excretion
Study Guide Respiration and excretion
Respiration and excretion  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key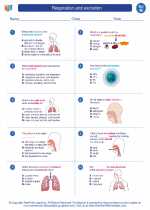 Respiration and excretion
Respiration and excretion  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key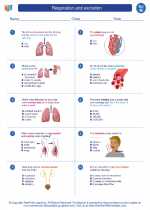 Respiration and excretion
Respiration and excretion  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key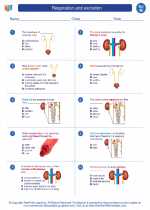 Respiration and excretion
Respiration and excretion  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Respiration and excretion
Respiration and excretion  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Respiration and excretion
Respiration and excretion  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Respiration and excretion
Respiration and excretion  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Respiration and excretion
Respiration and excretion 

 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
