Deserts
A desert is a landscape or region that receives very little precipitation, typically less than 250 millimeters (10 inches) per year. Deserts can be found on every continent and cover about one-fifth of the Earth's land surface. They are characterized by arid conditions, extreme temperatures, and sparse vegetation.
Types of Deserts
There are four main types of deserts:
- Hot and Dry Deserts: These deserts have high temperatures and very low humidity. Examples include the Sahara Desert in Africa and the Arabian Desert in the Middle East.
- Semiarid Deserts: These deserts have slightly more moisture than hot and dry deserts, but still experience long dry seasons. The Chihuahuan Desert in North America is an example of a semiarid desert.
- Coastal Deserts: Found along the coasts of continents, these deserts have moderate temperatures and low precipitation. The Atacama Desert in South America is a coastal desert.
- Cold Deserts: These deserts have low temperatures and can experience snowfall. The Gobi Desert in Asia is a cold desert.
Adaptations of Desert Plants and Animals
Plants and animals in deserts have developed unique adaptations to survive in the harsh conditions. Some common adaptations include:
- Water Conservation: Many desert plants have adaptations such as deep root systems and waxy coatings to minimize water loss.
- Nocturnal Behavior: Some desert animals are active at night to avoid the intense daytime heat.
- Burrowing: Many desert animals, such as rodents and reptiles, live underground to escape the extreme temperatures and reduce water loss.
- Camouflage: Both plants and animals have evolved to blend in with the desert environment to avoid predators.
Formation of Deserts
Deserts can form through various processes, including:
- Rain Shadow Effect: Mountains can block moisture-bearing winds, creating dry areas on the leeward side.
- Subsidence: High-pressure systems can lead to sinking air and dry conditions in certain regions.
- Continental Interior: Landlocked areas far from oceans can experience dry conditions due to limited moisture sources.
Human Impact on Deserts
Human activities, such as agriculture, urbanization, and resource extraction, can have significant impacts on desert ecosystems. Overgrazing, water diversion, and habitat destruction can lead to desertification, the process by which fertile land becomes desert. Conservation efforts and sustainable practices are important for protecting desert environments.
Study Tips
To study deserts effectively, consider the following tips:
- Use visual aids, such as maps and diagrams, to understand the distribution of deserts around the world.
- Learn about specific desert plants and animals and their unique adaptations for survival.
- Understand the factors that contribute to desert formation, such as climate patterns and geographic features.
- Explore the human impact on desert ecosystems and the importance of conservation efforts.
[Deserts] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Eighth Grade. Understanding Weather
 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson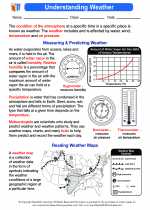
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
