Design
Design is the process of creating a plan or drawing for the construction of an object, system, or measurable human interaction. It involves a combination of creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills to develop a solution that meets certain criteria or objectives.
Types of Design
- Graphic Design: Involves creating visual content to communicate messages.
- Industrial Design: Focuses on the design of products and consumer goods.
- Interior Design: Deals with the design and decoration of interior spaces.
- Architectural Design: Involves designing buildings and structures.
- User Experience (UX) Design: Focuses on enhancing user satisfaction by improving the usability and accessibility of products and systems.
Elements of Design
The elements of design are the fundamental components that form the basis of any visual design. These elements include:
- Line: The path of a moving point.
- Shape: A two-dimensional area defined by other visual elements such as lines, color, and texture.
- Color: The visual perceptual property corresponding in humans to the categories called red, green, blue, and others.
- Texture: The tactile quality of a surface or the representation of such surfaces in art.
- Space: The distance or area between, around, above, below, or within things.
- Form: The volume and shape of a three-dimensional work.
- Value: The lightness or darkness of tones or colors.
Principles of Design
The principles of design are the guidelines that govern how the elements of design are combined. These principles include:
- Balance: Refers to the distribution of visual weight in a design.
- Emphasis: The part of the design that catches the viewer's attention.
- Contrast: The arrangement of opposite elements to create visual interest.
- Rhythm: A visual beat or pattern in the design created by the repetition of elements.
- Unity: The cohesive quality that makes the design feel complete and whole.
- Proportion: The relationship between elements in terms of size and scale.
- Harmony: The visually satisfying effect of combining similar elements.
Design Process
The design process typically involves the following steps:
- Research and Analysis: Understanding the problem, user needs, and constraints.
- Ideation: Generating a variety of ideas and potential solutions.
- Prototyping: Creating a preliminary version of the design to test and evaluate.
- Testing and Refinement: Gathering feedback and making improvements to the design.
- Implementation: Bringing the final design to life and integrating it into the intended context.
- Evaluation: Assessing the success of the design and identifying areas for further improvement.
Study Guide
To study design effectively, consider the following tips:
- Understand the difference between the various types of design and their specific characteristics.
- Memorize and comprehend the elements and principles of design to apply them in practical scenarios.
- Practice sketching and creating visual representations of design concepts to enhance your creativity and communication skills.
- Explore case studies and real-world examples of successful designs to understand the application of design principles and the design process.
- Engage in hands-on projects and design challenges to apply your knowledge and skills in a practical context.
By mastering the fundamentals of design and gaining practical experience, you can develop the ability to create effective and impactful designs across various disciplines.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Eighth Grade. Understanding Weather
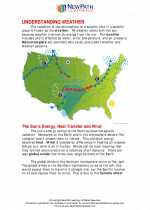
 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson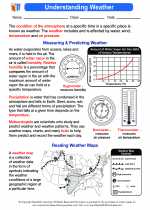
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
