Fats
Fats are an essential macronutrient that provide energy, support cell growth, protect organs, and help the body absorb nutrients. They are made up of fatty acids and serve as a rich source of energy, providing more than twice the amount of energy as carbohydrates and proteins.
Types of Fats
There are different types of fats, including:
- Saturated fats: These fats are typically solid at room temperature and are commonly found in animal products such as meat and dairy, as well as in some plant-based oils like coconut and palm oil.
- Unsaturated fats: These fats are usually in liquid form at room temperature and are primarily found in plant-based oils, such as olive oil, avocado oil, and canola oil. They are further classified into monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats.
- Trans fats: These fats are formed through a process called hydrogenation, which makes them more stable and gives them a longer shelf life. They are often found in processed foods and should be limited in the diet due to their negative impact on health.
Functions of Fats
Fats play several important roles in the body, including:
- Providing a source of energy
- Supporting cell growth
- Helping the body absorb fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K)
- Insulating the body to maintain body temperature
- Protecting organs
- Providing essential fatty acids that the body cannot produce on its own
Importance of Healthy Fats
Consuming healthy fats in moderation is essential for overall health. Foods rich in healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish, provide essential nutrients and can have a positive impact on heart health, brain function, and inflammation in the body.
Study Guide
When studying the topic of fats, it's important to focus on the following key points:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Eighth Grade. Understanding Weather
Study Guide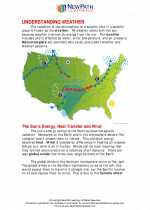 Understanding Weather
Understanding Weather  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson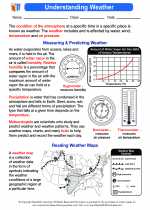 Understanding Weather
Understanding Weather  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Understanding Weather
Understanding Weather  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Understanding Weather
Understanding Weather  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Understanding Weather
Understanding Weather  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Understanding Weather
Understanding Weather  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Understanding Weather
Understanding Weather  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Understanding Weather
Understanding Weather  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Understanding Weather
Understanding Weather 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
Earth/Space Science: Students will use scientific skills and processes to explain the chemical and physical interactions (i.e., natural forces and cycles, transfer of energy) of the environment, Earth, and the universe that occur over time.
Interactions of Hydrosphere and Atmosphere: Cite evidence to explain the relationship between the hydrosphere and atmosphere.
Recognize and describe the water cycle as the distribution and circulation of Earth's water through the glaciers, surface water, groundwater, oceans, and atmosphere.