Galaxies
A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars, stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and dark matter. Galaxies come in various shapes and sizes and are the building blocks of the universe. They can range in size from dwarfs with as few as ten million stars to giants with one hundred trillion stars or more.
Types of Galaxies
There are three main types of galaxies:
- Elliptical Galaxies: These galaxies have an ellipsoidal shape and are characterized by their smooth, featureless appearance. They are made up of old stars and contain very little interstellar matter. Elliptical galaxies are classified based on their elongation, ranging from E0 (spherical) to E7 (highly elongated).
- Spiral Galaxies: Spiral galaxies are characterized by their flat, rotating disks and spiral arms. They contain a mix of old and young stars, as well as interstellar matter. The Milky Way is an example of a spiral galaxy.
- Irregular Galaxies: Irregular galaxies do not have a distinct shape and do not fit into the categories of elliptical or spiral galaxies. They often contain large amounts of interstellar matter and are sites of active star formation.
Galactic Structure
Galaxies are made up of various components, including:
- Stars: These are the basic building blocks of galaxies and are held together by gravity.
- Interstellar Matter: This includes gas and dust that fills the space between stars. It is the raw material for star formation.
- Dark Matter: This is a form of matter that does not emit or interact with electromagnetic radiation, but its presence is inferred from its gravitational effects on visible matter.
- Supermassive Black Holes: Many galaxies contain a supermassive black hole at their center, which can have millions or even billions of times the mass of the Sun.
Studying Galaxies
There are several methods that astronomers use to study galaxies:
- Observational Astronomy: This involves using telescopes and other instruments to observe the light and other forms of radiation emitted by galaxies.
- Computer Simulations: Scientists use computer simulations to model the formation and evolution of galaxies based on the laws of physics.
- Galaxy Classification: Astronomers classify galaxies based on their morphology, which provides insights into their formation and evolution.
- Redshift and Hubble’s Law: The redshift of galaxies, caused by the expansion of the universe, is used to measure their distances and velocities. This led to the discovery of Hubble's Law, which describes the relationship between a galaxy's distance and its velocity of recession.
Galactic Evolution
Galaxies evolve over time through processes such as star formation, interactions with other galaxies, and the accretion of intergalactic matter. Understanding galactic evolution helps astronomers piece together the history of the universe and the formation of structures within it.
Studying galaxies provides valuable insights into the nature of the universe, the formation of stars and planets, and the distribution of dark matter.
Study Guide
Here are some key points to remember when studying galaxies:
- Identify and describe the three main types of galaxies.
- Explain the components that make up galaxies, including stars, interstellar matter, dark matter, and supermassive black holes.
- Discuss the methods used by astronomers to study galaxies, such as observational astronomy, computer simulations, and galaxy classification.
- Understand the concept of galactic evolution and its importance in understanding the history and structure of the universe.
- Be familiar with the contributions of Hubble's Law and the redshift of galaxies to our understanding of cosmic expansion.
By mastering these concepts, you will have a solid understanding of galaxies and their significance in the study of astronomy and cosmology.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Eighth Grade. Understanding Weather
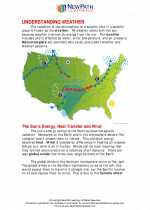
 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson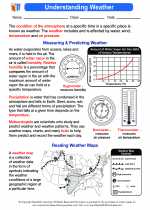
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
