What is a Landslide?
A landslide is the movement of rock, soil, and debris down a slope. It can happen suddenly or gradually and is often caused by a variety of factors, including heavy rainfall, earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and human activities.
Causes of Landslides
Landslides can be triggered by natural and human-induced factors:
- Natural Causes: Heavy rainfall, snowmelt, earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and erosion can destabilize the slope and lead to a landslide.
- Human-induced Causes: Deforestation, construction activities, mining, and improper land use can weaken the stability of the slope and increase the risk of landslides.
Types of Landslides
There are several types of landslides, including:
- Rock Falls: Sudden collapse of rocks from a steep slope.
- Debris Flows: Rapid movement of water-saturated debris down a slope.
- Slumps: Movement of a mass of rock or soil along a curved surface.
- Earth Flows: Slow to rapid movement of water-saturated soil and debris.
Effects of Landslides
Landslides can have devastating effects, including:
- Property Damage: Destruction of homes, roads, and infrastructure.
- Loss of Life: Landslides can cause fatalities and injuries.
- Environmental Impact: Alteration of landscapes, disruption of ecosystems, and sedimentation of water bodies.
- Economic Consequences: Costly cleanup and restoration efforts, as well as long-term economic impacts on communities.
Preventing and Mitigating Landslides
Several measures can be taken to prevent and mitigate the impact of landslides:
- Land Use Planning: Identifying and avoiding high-risk areas for development.
- Vegetation Management: Planting trees and vegetation to stabilize slopes and reduce erosion.
- Engineering Solutions: Building retaining walls, barriers, and drainage systems to control slope stability.
- Early Warning Systems: Monitoring and alerting systems to provide advance notice of potential landslides.
Study Guide
Use the following questions to guide your study of landslides:
- What are the natural and human-induced causes of landslides?
- Describe the different types of landslides and their characteristics.
- What are the effects of landslides on the environment and human settlements?
- Discuss the measures that can be taken to prevent and mitigate the impact of landslides.
- Research a historic landslide event and analyze its causes, effects, and the response of the affected community.
By understanding the causes, types, effects, and prevention strategies related to landslides, you can develop a comprehensive knowledge of this natural hazard and its impact on the environment and society.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Eighth Grade. Understanding Weather
Study Guide Understanding Weather
Understanding Weather  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson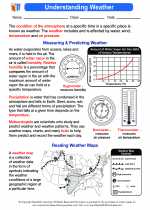 Understanding Weather
Understanding Weather  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Understanding Weather
Understanding Weather  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Understanding Weather
Understanding Weather  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Understanding Weather
Understanding Weather  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Understanding Weather
Understanding Weather  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Understanding Weather
Understanding Weather  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Understanding Weather
Understanding Weather  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Understanding Weather
Understanding Weather 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
Earth/Space Science: Students will use scientific skills and processes to explain the chemical and physical interactions (i.e., natural forces and cycles, transfer of energy) of the environment, Earth, and the universe that occur over time.
Interactions of Hydrosphere and Atmosphere: Cite evidence to explain the relationship between the hydrosphere and atmosphere.
Recognize and describe the water cycle as the distribution and circulation of Earth's water through the glaciers, surface water, groundwater, oceans, and atmosphere.