Landforms
Landforms are natural features of the Earth's surface. They are created by various geological processes such as erosion, weathering, and plate tectonics. Studying landforms is important as it helps us understand the Earth's history and the forces that continue to shape our planet.
Types of Landforms
There are several types of landforms, each with its own unique characteristics. Some of the key landforms include:
- Mountains: These are landforms that rise prominently above their surroundings, typically with steep slopes and a peak or summit.
- Valleys: Valleys are low-lying areas between mountains or hills, often carved out by rivers or glaciers.
- Plateaus: Plateaus are elevated flat areas of land, often with steep sides.
- Plains: Plains are extensive flat areas of land with minimal changes in elevation.
- Deserts: Deserts are dry, arid regions with sparse vegetation and little precipitation.
- Coastlines: Coastlines are the boundary between land and sea, characterized by features such as beaches, cliffs, and bays.
- Islands: Islands are landforms that are completely surrounded by water.
Formation of Landforms
Landforms are created through a variety of natural processes. Some of the key processes that contribute to the formation of landforms include:
- Erosion: The wearing away of the Earth's surface by water, wind, or ice.
- Weathering: The breakdown of rocks and minerals at or near the Earth's surface.
- Volcanism: The eruption of molten rock, ash, and gases from the Earth's interior, leading to the formation of mountains, volcanoes, and other landforms.
- Plate Tectonics: The movement of the Earth's lithospheric plates, leading to the formation of mountains, valleys, and other landforms.
Studying Landforms
There are various methods for studying landforms, including:
- Field Observations: Visiting and observing landforms in their natural environment.
- Maps and Aerial Imagery: Using maps and aerial imagery to study the distribution and characteristics of landforms.
- Geological Surveys: Conducting surveys to gather detailed information about the composition and structure of landforms.
- Remote Sensing: Using satellite and airborne sensors to collect data about landforms from a distance.
Understanding landforms is essential for various fields of study, including geography, geology, and environmental science. It allows us to appreciate the diversity of the Earth's surface and the dynamic processes that continue to shape it.
Now that we have an understanding of landforms, let's move on to the study guide for this topic:
Landforms Study Guide
- Define the term "landform" and provide examples of different types of landforms.
- Explain the processes involved in the formation of landforms, including erosion, weathering, and plate tectonics.
- Discuss the significance of studying landforms and how it contributes to our understanding of the Earth's surface.
- Identify and describe the methods used to study landforms, such as field observations, maps, and remote sensing.
- Choose a specific landform and create a presentation or report detailing its characteristics, formation, and significance.
By completing this study guide, you will have a comprehensive understanding of landforms and the processes that shape our planet's surface.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Kindergarten. All About Animals
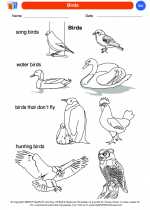
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet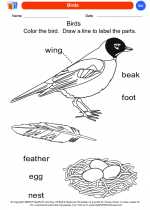
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet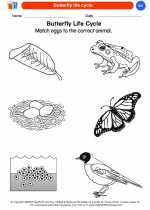
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet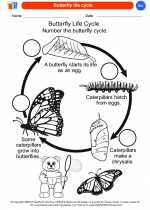
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet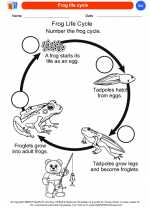
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet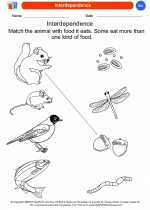
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet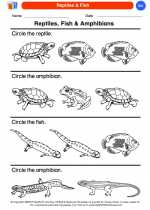
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet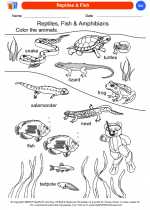
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
