Macrolides in Science
Macrolides are a class of antibiotics that are commonly used to treat bacterial infections. They work by inhibiting the growth and reproduction of bacteria, making them effective in fighting off a wide range of bacterial illnesses.
How do Macrolides Work?
Macrolides work by binding to the bacterial ribosome, which is the part of the cell responsible for protein synthesis. By binding to the ribosome, macrolides prevent the bacteria from producing essential proteins, ultimately leading to their inability to grow and reproduce.
Common Macrolide Antibiotics
Some common macrolide antibiotics include:
- Erythromycin
- Azithromycin
- Clarithromycin
Usage and Side Effects
Macrolide antibiotics are commonly used to treat respiratory tract infections, skin infections, and other bacterial illnesses. However, they may have side effects such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. It's important to use them as prescribed by a healthcare professional.
Study Guide
Here are some key points to remember about macrolides:
- Macrolides are antibiotics that inhibit bacterial growth.
- They work by binding to the bacterial ribosome.
- Common macrolide antibiotics include erythromycin, azithromycin, and clarithromycin.
- They are used to treat respiratory and skin infections.
- Side effects may include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Kindergarten. All About Animals
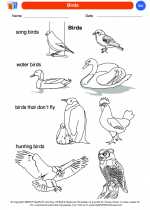
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet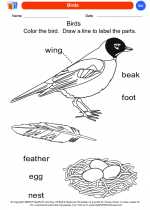
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet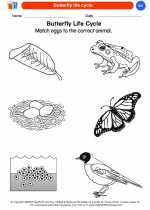
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet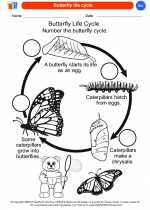
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet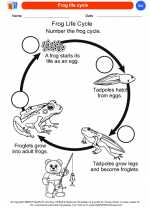
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet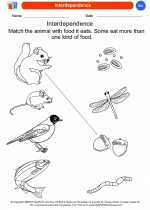
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet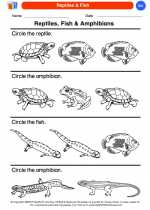
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet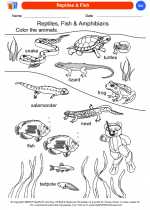
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
