Rain Gauge Study Guide
What is a Rain Gauge?
A rain gauge is a meteorological instrument used to measure the amount of precipitation, typically in the form of rain, that falls at a particular location over a specific period of time.
How Does a Rain Gauge Work?
A rain gauge works by collecting and measuring the amount of liquid precipitation that falls within a specific time period. The most common type of rain gauge is the standard cylindrical rain gauge, which consists of a graduated cylinder that collects and measures the rainfall.
Types of Rain Gauges
There are several types of rain gauges, including:
- Standard Rain Gauge: This is the most common type of rain gauge, consisting of a graduated cylinder to measure the rainfall.
- Tipping Bucket Rain Gauge: This type of rain gauge uses a funnel to direct the rain into a small bucket. When a certain amount of water collects in the bucket, it tips and empties, recording the rainfall amount.
- Weighing Rain Gauge: This type of rain gauge measures the weight of the collected rainfall to determine the precipitation amount.
Why are Rain Gauges Important?
Rain gauges are important because they provide essential data for meteorologists, hydrologists, and climatologists to monitor and analyze rainfall patterns, predict floods, and manage water resources. This information is crucial for agriculture, water supply management, and weather forecasting.
How to Use a Rain Gauge?
To use a rain gauge, follow these steps:
- Place the rain gauge in an open area, away from obstructions such as buildings or trees.
- Check the rain gauge regularly and record the amount of rainfall at the same time each day.
- Empty the rain gauge after each measurement to prepare for the next rainfall.
Fun Fact
Did you know that the first known rainfall records were kept by the Ancient Greeks over 2,500 years ago using a simple measuring vessel?
[Rain Gauge] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Kindergarten. All About Animals
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet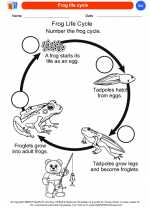
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet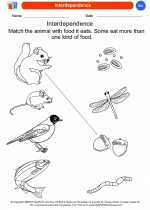
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet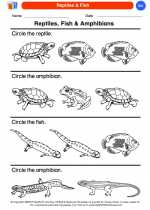
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet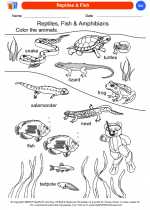
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
