Systems in Science
In science, a system is a group of interacting, interrelated, or interdependent components that form a complex and unified whole. Systems can be found in all areas of science and are used to understand the interconnectedness and behavior of different processes and phenomena.
Types of Systems
There are different types of systems, including:
- Open Systems: Systems that can exchange both matter and energy with their surroundings.
- Closed Systems: Systems that can exchange energy but not matter with their surroundings.
- Isolated Systems: Systems that do not exchange energy or matter with their surroundings.
Examples of Systems
Examples of systems in science include the human body (a biological system), the water cycle (an environmental system), and the solar system (an astronomical system).
Studying Systems
To study systems, scientists use system analysis, which involves examining the components of a system, their interactions, and the behaviors that emerge from these interactions. This helps in understanding the system's properties and predicting its behavior.
Study Guide: Exploring Systems in Science
- Define the term "system" in the context of science. Provide examples of systems from different scientific disciplines (e.g., biology, ecology, astronomy).
- Discuss the different types of systems (open, closed, isolated) and provide real-world examples of each type.
- Explain the concept of system analysis and its importance in studying complex systems. Provide an example of how system analysis can be used to understand a specific system.
- Identify and describe a system of your choice, detailing its components, interactions, and emergent behaviors. Discuss why understanding this system is important in the context of science.
Understanding systems is crucial in various scientific fields, and studying them helps in unraveling the complexities of the natural world.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Kindergarten. All About Animals
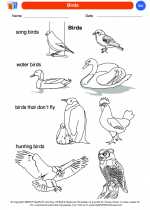
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet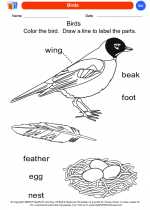
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet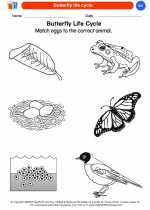
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet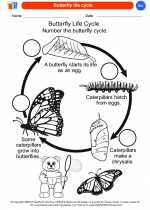
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet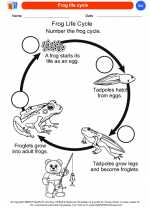
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet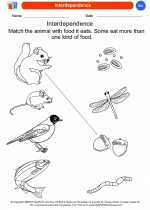
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet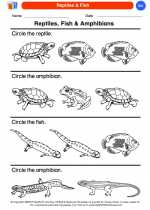
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet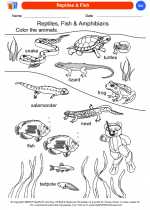
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
