Tissues
In biology, tissues are groups of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function. There are four main types of tissues in the human body: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissues.
Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial tissue covers the body's surfaces and lines its cavities. It serves as a protective barrier and can be found in the skin, the lining of the digestive tract, and the lining of blood vessels.
Connective Tissue
Connective tissue provides support and connects different parts of the body. It includes bone, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, and adipose tissue (fat). Blood is also considered a type of connective tissue.
Muscle Tissue
Muscle tissue is responsible for movement. There are three types of muscle tissue: skeletal muscle (attached to bones and responsible for voluntary movement), smooth muscle (found in the walls of internal organs and blood vessels), and cardiac muscle (found in the heart).
Nervous Tissue
Nervous tissue is found in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. It is made up of neurons and is responsible for transmitting and receiving signals throughout the body, allowing for communication and coordination of bodily functions.
Study Guide
- What are tissues?
- What are the four main types of tissues in the human body?
- Describe the function of epithelial tissue.
- Provide examples of connective tissue.
- How many types of muscle tissue are there, and what are they?
- Where is nervous tissue found, and what is its function?
[Tissues] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Kindergarten. All About Plants

 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet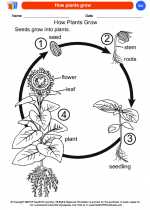
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet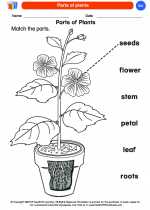
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet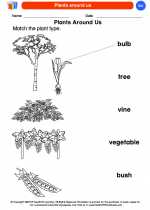
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet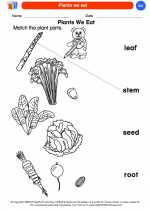
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
