Cephalosporins Study Guide
What are Cephalosporins?
Cephalosporins are a type of antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections. They are derived from a fungus and are related to penicillin.
Mechanism of Action
Cephalosporins work by disrupting the cell wall of bacteria, leading to their death. They are bactericidal, meaning they kill the bacteria rather than just inhibiting their growth.
Generations of Cephalosporins
Cephalosporins are divided into five generations based on their spectrum of activity and when they were developed. Each generation has a broader spectrum of activity than the previous one.
Common Uses
Cephalosporins are used to treat a wide range of bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, urinary tract infections, and more severe infections such as sepsis and meningitis.
Safety and Side Effects
Cephalosporins are generally safe and well-tolerated, but they can cause side effects such as diarrhea, nausea, and allergic reactions in some individuals. It's important to use them only as prescribed by a healthcare professional.
Drug Interactions
Cephalosporins can interact with other medications, so it's important to inform your healthcare provider about all the medications you are taking before starting cephalosporin treatment.
Conclusion
Cephalosporins are an important class of antibiotics that are widely used to treat bacterial infections. Understanding their mechanism of action, generations, common uses, and potential side effects is important for anyone studying or working in the field of medicine.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Kindergarten. Our Earth
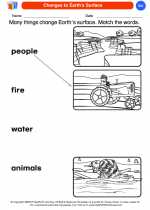
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet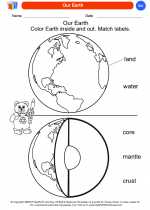
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet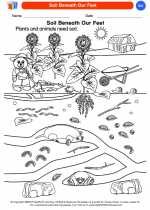
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
