Our Earth -> reproductive organs
Reproductive Organs
The reproductive system is a collection of internal and external organs — in both males and females — that work together for the purpose of procreating. These organs are responsible for the production of gametes (sperm and eggs) and the secretion of sex hormones. Understanding the reproductive organs is important for understanding human growth and development.
Male Reproductive Organs
The male reproductive system includes the following organs:
- Testes: These are the primary male reproductive organs responsible for producing sperm and testosterone.
- Epididymis: This is a coiled tube located on the back of each testis where sperm is stored and matured.
- Vas Deferens: Also known as the sperm duct, this tube carries sperm from the epididymis to the urethra.
- Prostate Gland: This gland produces a fluid that helps protect and nourish sperm.
- Seminal Vesicles: These glands produce a fluid that mixes with sperm to form semen.
- Penis: The external male reproductive organ that is involved in sexual intercourse and the release of urine.
Female Reproductive Organs
The female reproductive system includes the following organs:
- Ovaries: These are the primary female reproductive organs responsible for producing eggs and female sex hormones, including estrogen and progesterone.
- Fallopian Tubes: These tubes transport eggs from the ovaries to the uterus and provide the site for fertilization by sperm.
- Uterus: Also known as the womb, the uterus is where a fertilized egg implants and develops into a fetus during pregnancy.
- Cervix: The lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina.
- Vagina: The muscular tube that connects the external genitals to the cervix and serves as the birth canal and the site for menstrual flow.
Study Guide
When studying the reproductive organs, it's important to understand the functions of each organ, as well as their roles in the process of reproduction. Practice labeling diagrams of the male and female reproductive systems to familiarize yourself with the location and structure of each organ. Additionally, familiarize yourself with the processes of spermatogenesis and oogenesis, which are the production of sperm and eggs, respectively.
Understanding the reproductive organs is crucial for comprehending human reproduction, fertility, and the changes that occur during puberty. It also forms the foundation for understanding topics such as contraception, fertility treatments, and reproductive health.
[Reproductive Organs] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Kindergarten. Our Earth
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet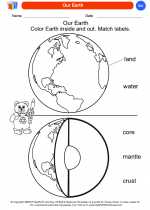
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
