Decimals
Decimals are a way of representing a part of a whole number. They are used to express numbers that are not whole, such as fractions or portions of a whole. In a decimal number, a dot (.) is used to separate the whole number part from the fractional part.
Place Value of Decimals
Each digit in a decimal number has a specific place value based on its position to the right of the decimal point. The place values of decimal digits are powers of 10, with the value decreasing from left to right as follows: tenths, hundredths, thousandths, and so on.
Converting Decimals
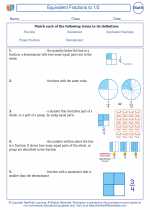
Decimals can be converted to fractions and vice versa. To convert a decimal to a fraction, the decimal number is written as the numerator, and the place value of the rightmost digit becomes the denominator. For example, 0.5 is equivalent to 5/10, which simplifies to 1/2.
Operations with Decimals
Decimals can be added, subtracted, multiplied, and divided following similar rules to whole numbers. When performing these operations, it is important to align the decimal points and adjust the number of decimal places in the result accordingly.
Real-Life Applications
Decimals are used in various real-life situations, such as measuring lengths, weights, and volumes, calculating money, and representing percentages.
[Decimals] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
.◂Math Worksheets and Study Guides Second Grade. Fractions Greater Than or Less Than 1/2
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key