Equations
An equation is a mathematical statement that shows the equality between two expressions. It consists of an equal sign (=) between the two expressions. The goal of solving an equation is to find the value of the unknown variable that makes the equation true.
Parts of an equation:
An equation consists of the following parts:
- Left-hand side (LHS): This is the expression on the left side of the equal sign.
- Right-hand side (RHS): This is the expression on the right side of the equal sign.
- Equal sign (=): This symbol indicates that the LHS is equal to the RHS.
- Unknown variable: This is the variable whose value we want to find. It is usually represented by a letter such as x, y, or z.
Types of equations:
Equations can be classified into different types based on their degree and number of variables. Some common types of equations include:
- Linear equations: These are equations of the form ax + b = c, where a, b, and c are constants, and x is the unknown variable. The highest power of the variable is 1.
- Quadratic equations: These are equations of the form ax2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are constants, and x is the unknown variable. The highest power of the variable is 2.
- Systems of equations: These are a set of two or more equations with the same variables. The solution to the system is the set of values that satisfy all the equations simultaneously.
Solving equations:
To solve an equation, we perform operations on both sides of the equation to isolate the variable and find its value. The goal is to get the variable alone on one side of the equation. The operations we can use include addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and taking square roots.
Example:
Let's solve the equation 3x - 7 = 8.
First, we want to isolate the variable x. We can do this by adding 7 to both sides of the equation:
3x - 7 + 7 = 8 + 7
3x = 15
Then, we divide both sides by 3 to solve for x:
x = 5
So, the solution to the equation is x = 5.
Equations are fundamental in mathematics and are used to model and solve a wide range of real-world problems.
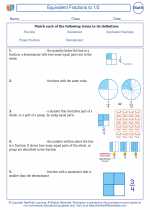
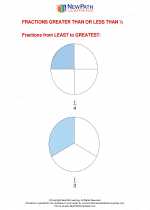
.◂Math Worksheets and Study Guides Second Grade. Fractions Greater Than or Less Than 1/2
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key