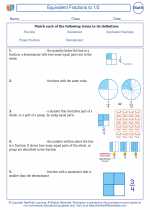
Right Triangle
A right triangle is a type of triangle that has one angle measuring 90 degrees, which is called a right angle. The side opposite the right angle is called the hypotenuse, and the other two sides are called the legs.
The Pythagorean theorem, which is a fundamental principle in geometry, states that in a right triangle, the sum of the squares of the lengths of the two legs is equal to the square of the length of the hypotenuse. This can be expressed in the formula:
a2 + b2 = c2
where 'a' and 'b' are the lengths of the legs, and 'c' is the length of the hypotenuse.
Right triangles are commonly used in geometry and trigonometry to solve various problems, such as finding unknown side lengths or angles using trigonometric functions like sine, cosine, and tangent.
Understanding the properties and theorems related to right triangles is essential for solving many mathematical problems and for applications in fields such as engineering, architecture, and physics.
Overall, right triangles are an important and foundational concept in mathematics with wide-ranging practical implications.
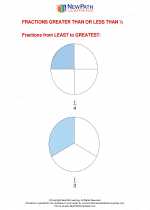
.◂Math Worksheets and Study Guides Second Grade. Fractions Greater Than or Less Than 1/2
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key