Solar Calendar
A solar calendar is a calendar system based on the Earth's position relative to the Sun. It is used to track the passage of time and to organize and plan activities throughout the year.
The most well-known solar calendar is the Gregorian calendar, which is widely used around the world today. The Gregorian calendar is based on the Earth's orbit around the Sun, with a year consisting of 365 days (366 days in a leap year).
Solar calendars are typically divided into months, with the length of each month corresponding to the time it takes for the Earth to complete one orbit around the Sun. This results in a total of 12 months in a year.
One of the key features of a solar calendar is the establishment of leap years, which occur approximately every four years to account for the extra quarter of a day in the Earth's orbit. This helps to keep the calendar in alignment with the changing seasons over time.
By using a solar calendar, people can schedule and plan events, agricultural activities, religious observances, and other important occasions based on the Earth's position in its orbit around the Sun.
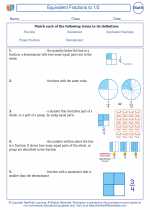
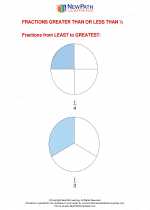
.◂Math Worksheets and Study Guides Second Grade. Fractions Greater Than or Less Than 1/2
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key