Understanding a Day
A day is a unit of time that is based on the Earth's rotation. It is the time it takes for the Earth to complete one full rotation on its axis. This rotation causes day and night to occur, as different parts of the Earth are exposed to the Sun's light at different times. Understanding the concept of a day is essential for understanding time and calendars.
Key Concepts:
- 24 Hours: A day is typically divided into 24 hours, each hour consisting of 60 minutes.
- Day and Night: The rotation of the Earth causes the cycle of day and night. When a specific location on Earth is facing the Sun, it experiences daytime, while the opposite side experiences nighttime.
- International Date Line: This imaginary line marks the change in calendar days. Crossing the International Date Line can result in a day being gained or lost, depending on the direction of travel.
- Solar Noon: This is the time of day when the Sun reaches its highest point in the sky. It divides the day into two equal halves, with morning before solar noon and afternoon after solar noon.
Study Guide:
Here are some key points to focus on when studying the concept of a day:
- What causes day and night?
- How is a day divided into smaller units of time?
- What is the significance of the International Date Line?
- How does the concept of a day relate to the Earth's rotation?
Understanding the concept of a day is fundamental to comprehending timekeeping and the measurement of days, weeks, months, and years. It also plays a crucial role in various fields such as astronomy, geography, and navigation.
.◂Math Worksheets and Study Guides Fifth Grade. Common Factors
Study Guide Common Factors
Common Factors  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Common Factors
Common Factors  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Common Factors
Common Factors  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Common Factors
Common Factors  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Greatest Common Factor of numbers not greater than 24
Greatest Common Factor of numbers not greater than 24  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Magic Squares
Magic Squares  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Star Mathematics
Star Mathematics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key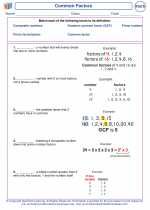 Common Factors
Common Factors 

 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
Algebra (NCTM)
Use mathematical models to represent and understand quantitative relationships.
Model problem situations with objects and use representations such as graphs, tables, and equations to draw conclusions.