One-Dimensional
One-dimensional refers to a single dimension or direction. In mathematics, it typically refers to a line or a straight path with no width or depth. Understanding one-dimensional concepts is important in various mathematical and scientific fields.
Key Points:
- Definition: One-dimensional refers to a linear or straight path with no width or depth.
- Examples: A straight line, a number line, and motion along a single axis are all examples of one-dimensional concepts.
- Coordinates: In a one-dimensional space, points can be represented by a single coordinate on a number line.
- Applications: One-dimensional concepts are used in physics, geometry, and computer science, among other fields.
- Visualizing: Visualizing one-dimensional objects and their movements can help in understanding mathematical concepts and solving problems.
Study Guide:
To better understand the concept of one-dimensional, consider the following study guide:
- Number Line: Practice plotting points and understanding their positions on a number line. This will help in visualizing one-dimensional space.
- Real-Life Examples: Look for real-life examples of one-dimensional motion or objects, such as a car moving along a straight road or a ruler placed on a table.
- Coordinate Systems: Familiarize yourself with coordinate systems and how they are used to represent points in one-dimensional space.
- Problem Solving: Solve problems that involve one-dimensional concepts, such as calculating distances along a straight path or determining positions on a number line.
- Mathematical Models: Explore mathematical models that use one-dimensional representations, such as linear equations and inequalities.
By mastering the concepts and applications of one-dimensional, you'll be better equipped to understand linear relationships, motion along a single axis, and other mathematical and scientific principles.
.◂Math Worksheets and Study Guides Fifth Grade. Common Factors
Study Guide Common Factors
Common Factors  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Common Factors
Common Factors  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Common Factors
Common Factors  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Common Factors
Common Factors  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Greatest Common Factor of numbers not greater than 24
Greatest Common Factor of numbers not greater than 24  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Magic Squares
Magic Squares  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Star Mathematics
Star Mathematics  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key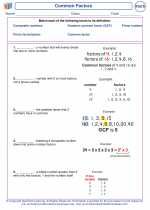 Common Factors
Common Factors 

 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
Algebra (NCTM)
Use mathematical models to represent and understand quantitative relationships.
Model problem situations with objects and use representations such as graphs, tables, and equations to draw conclusions.