Weather Study Guide
Weather refers to the current state of the atmosphere at a specific place and time. It is influenced by various factors and can change frequently. Understanding weather is important for predicting and preparing for different conditions.
Key Concepts
- Atmosphere: The layer of gases that surround the Earth. It includes air, water vapor, and other substances.
- Temperature: A measure of how hot or cold the air is. It is usually measured in degrees Celsius or Fahrenheit.
- Precipitation: Any form of water, liquid or solid, that falls from the atmosphere and reaches the ground. This includes rain, snow, sleet, and hail.
- Humidity: The amount of water vapor present in the air. It affects how comfortable or uncomfortable the air feels.
- Wind: The movement of air from an area of high pressure to an area of low pressure. It can be calm or strong, and it is measured in terms of speed and direction.
- Weather Patterns: Regularly occurring weather conditions, such as seasonal changes, that can be observed over a specific period of time.
Weather Instruments
Scientists use various tools to measure and monitor weather conditions. Some common weather instruments include:
- Thermometer: Measures temperature.
- Barometer: Measures air pressure.
- Anemometer: Measures wind speed and direction.
- Rain gauge: Measures the amount of precipitation.
- Hygrometer: Measures humidity levels.
Types of Weather
Weather can be classified into different types based on the conditions observed. Some common types of weather include:
- Sunny: Clear skies with abundant sunlight.
- Cloudy: Overcast skies with limited or no sunlight.
- Rainy: Precipitation in the form of rain.
- Snowy: Precipitation in the form of snow.
- Stormy: Severe weather conditions including thunderstorms, lightning, and strong winds.
Effects of Weather
Weather has significant impacts on various aspects of our lives, including:
- Agriculture: Weather conditions can influence crop growth and yield.
- Transportation: Severe weather can disrupt travel and cause delays.
- Health: Extreme temperatures and weather events can affect human health.
- Environment: Weather patterns can impact natural ecosystems and habitats.
Conclusion
Understanding weather is crucial for making informed decisions and staying safe in different conditions. By learning about weather patterns and phenomena, we can better prepare for and adapt to the ever-changing atmosphere around us.
[Weather] Related Worksheets and Study Guides:
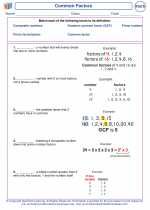
.◂Math Worksheets and Study Guides Fifth Grade. Common Factors

 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key