Right Triangle
A right triangle is a geometric shape that has one angle equal to 90 degrees. The side opposite the right angle is called the hypotenuse, and the other two sides are known as the legs of the triangle.
The Pythagorean theorem, which is a fundamental principle in geometry, states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (c) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides (a and b). This can be represented by the formula:
c2 = a2 + b2
Right triangles have many applications in mathematics, physics, and engineering, and they are widely used in solving various real-world problems involving distance, height, and angles.
.◂Math Worksheets and Study Guides Kindergarten. Sort, classify, and order objects
Coloring Worksheet Big or Little
Big or Little  Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet Few & Many
Few & Many  Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet Full & Empty
Full & Empty  Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet Hot & Cold
Hot & Cold  Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet Long & Short
Long & Short  Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet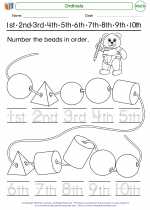 Ordinals
Ordinals  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Heavy or Light
Heavy or Light  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Assessment
Assessment  Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet Big or Little
Big or Little  Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet Full & Empty
Full & Empty  Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet Hot & Cold
Hot & Cold  Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet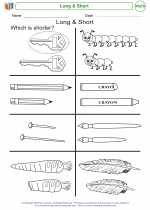 Long & Short
Long & Short  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Assessment
Assessment  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key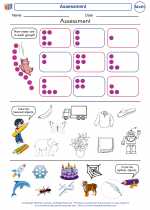 Assessment
Assessment  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Assessment
Assessment  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key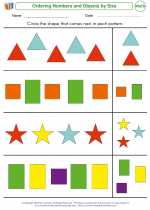 Ordering Numbers and Objects by Size
Ordering Numbers and Objects by Size  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key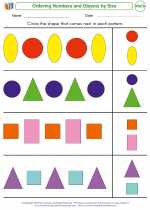 Ordering Numbers and Objects by Size
Ordering Numbers and Objects by Size  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key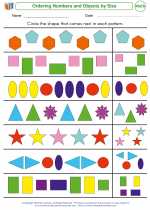 Ordering Numbers and Objects by Size
Ordering Numbers and Objects by Size  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Data
Data  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Data
Data 

 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Coloring Worksheet
Coloring Worksheet
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
Measurement and Data
Describe and compare measurable attributes.
Directly compare two objects, with a measurable attribute in common, to see which object has “more of” or “less of” the attribute, and describe the difference. [K-MD2]
Classify objects and count the number of objects in each category.
Classify objects into given categories; count the number of objects in each category, and sort the categories by count. (Limit category counts to be less than or equal to 10.) [K-MD3]