Organelles
Organelles are specialized structures within a cell that perform specific functions to ensure the cell's survival and proper functioning. Each organelle has its own unique structure and function, and they work together to carry out various cellular processes.
Nucleus
The nucleus is often referred to as the control center of the cell. It houses the cell's genetic material, DNA, and is responsible for regulating all cellular activities. The nucleus is surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope, which contains pores that allow for the exchange of materials between the nucleus and the rest of the cell.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes that is involved in the synthesis and transport of proteins and lipids. There are two types of ER: rough ER, which is studded with ribosomes and involved in protein synthesis, and smooth ER, which is involved in lipid metabolism and detoxification of drugs and poisons.
Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus is responsible for modifying, sorting, and packaging proteins and lipids for transportation to their final destination within or outside the cell. It consists of a series of flattened membrane-bound sacs called cisternae.
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are often referred to as the powerhouse of the cell because they are the sites of cellular respiration, where energy is produced in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). They have a double membrane and their own DNA, suggesting that they may have originated from an independent organism through a process called endosymbiosis.
Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts are found in plant cells and are responsible for carrying out photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose. They contain a green pigment called chlorophyll, which gives plants their characteristic green color.
Vacuoles
Vacuoles are membrane-bound organelles that are involved in storage, waste management, and maintaining turgor pressure in plant cells. They can store water, nutrients, and waste products, and play a role in maintaining the cell's shape and structure.
Lysosomes
Lysosomes are membrane-bound vesicles that contain digestive enzymes. They are involved in breaking down and recycling cellular waste and debris, as well as in the digestion of engulfed food particles and invading microorganisms.
Studying organelles can be fascinating and can deepen your understanding of how cells function and maintain life. To help you remember the key points about organelles, here's a study guide:
Organelles Study Guide
- What is the function of the nucleus?
- Describe the structure and function of the endoplasmic reticulum.
- What is the role of the Golgi apparatus in the cell?
- Why are mitochondria often referred to as the powerhouse of the cell?
- What is the main function of chloroplasts?
- What are the functions of vacuoles in plant cells?
- Explain the role of lysosomes in cellular processes.
Answering these questions will help reinforce your understanding of organelles and their functions within the cell.
Happy studying!
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides First Grade. Human body

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson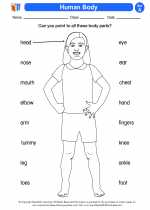
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key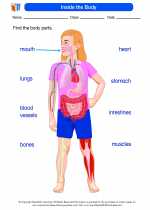
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key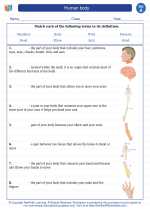
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
