Grasses
Grasses are a type of plant that belong to the Poaceae family. They are found in many different habitats, from prairies and savannas to mountains and forests. There are over 10,000 species of grasses, making them one of the most diverse plant families on Earth.
Structure of Grasses
Grasses have a unique structure that sets them apart from other plants. They typically have long, narrow leaves with parallel veins. Their stems are hollow and round, which gives them flexibility and strength. Grasses also have a fibrous root system that helps them anchor into the ground and absorb water and nutrients.
Importance of Grasses
Grasses play a crucial role in many ecosystems. They provide food for a variety of animals, including grazing mammals and insects. In addition, grasses help prevent soil erosion, maintain water quality, and contribute to the overall health of the environment. Humans also rely on grasses for food, as many grains such as wheat, rice, and corn are members of the grass family.
Life Cycle of Grasses
Grasses reproduce through seeds, which are typically produced in the flowers of the plant. The seeds can be dispersed by wind, water, or animals, helping the grasses spread to new locations. Once the seeds germinate, the grasses go through a life cycle that includes stages such as seedling, vegetative growth, flowering, and seed production.
Study Guide
- What family do grasses belong to?
- Describe the structure of grasses.
- Explain the importance of grasses in ecosystems.
- How do grasses reproduce?
- Discuss the life cycle of grasses.
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides First Grade. Weather

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson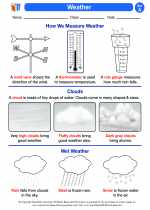
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
