Titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. It is a strong, lustrous, and corrosion-resistant transition metal with a silver color. Titanium is known for its high strength-to-weight ratio, which makes it ideal for a wide range of applications, from aerospace and military to medical and consumer products.
Physical and Chemical Properties
- Atomic number: 22
- Atomic symbol: Ti
- Atomic weight: 47.867
- State at room temperature: Solid
- Melting point: 1,668°C (3,034°F)
- Boiling point: 3,287°C (5,949°F)
- Density: 4.5 g/cm³
- Electron configuration: [Ar] 3d2 4s2
- Oxidation states: +2, +3, +4
Uses of Titanium
Titanium is widely used in various industries due to its exceptional properties. Some common uses of titanium include:
- Aeronautics and aerospace: Titanium's high strength and low density make it ideal for aircraft and spacecraft components.
- Medical implants: Titanium is biocompatible, making it suitable for use in surgical implants such as joint replacements and dental implants.
- Sports equipment: Titanium is used in the production of high-performance sports equipment such as bicycle frames, golf clubs, and tennis rackets.
- Chemical processing: Titanium's corrosion resistance makes it valuable in chemical processing plants and desalination facilities.
Study Guide
Here are some key points to remember about titanium:
- Atomic number and symbol: Titanium has the atomic number 22 and the symbol Ti.
- Physical properties: Titanium is a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, a melting point of 1,668°C, and a density of 4.5 g/cm³.
- Chemical properties: Titanium has multiple oxidation states (+2, +3, +4) and an electron configuration of [Ar] 3d2 4s2.
- Uses: Titanium is used in aerospace, medical implants, sports equipment, and chemical processing.
Remember to review these key points and explore the various applications of titanium in different industries.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides First Grade. Weather
Study Guide Weather
Weather  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson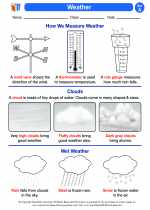 Weather
Weather  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Weather
Weather  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Weather
Weather  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Weather
Weather  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Weather
Weather  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Weather
Weather  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Weather
Weather 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
Earth Systems Science
Earth's materials can be compared and classified based on their properties. Students can:
Identify and represent similarities and differences such as the texture, size, color, and shape of various materials on Earth