Bioenergy
Bioenergy is a form of renewable energy derived from organic materials, also known as biomass. Biomass can include organic materials such as wood, agricultural residues, and even municipal solid waste. Bioenergy can be harnessed through various processes, such as combustion, fermentation, and anaerobic digestion, to produce heat, electricity, or transportation fuels.
Types of Bioenergy
There are several types of bioenergy, including:
- Biofuels: These are liquid or gaseous fuels derived from biomass, such as ethanol, biodiesel, and biogas.
- Bioelectricity: This is electricity generated from biomass through processes like combustion or gasification.
- Biopower: This involves the direct combustion of biomass to produce heat and power.
Benefits of Bioenergy
There are several benefits associated with bioenergy:
- Renewable: Biomass is a renewable resource, as long as it is managed sustainably.
- Reduction of Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Bioenergy can contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, especially when compared to fossil fuels.
- Waste Management: Bioenergy can be produced from organic waste materials, providing a means of waste management and reducing landfill usage.
- Energy Security: Bioenergy can contribute to diversifying energy sources and reducing dependence on imported fossil fuels.
Study Guide
To understand bioenergy in more depth, consider the following study guide:
- Define bioenergy and explain its significance as a renewable energy source.
- Compare and contrast different types of bioenergy, such as biofuels, bioelectricity, and biopower.
- Discuss the environmental benefits of bioenergy and its potential contribution to mitigating climate change.
- Examine the challenges and limitations associated with bioenergy production and utilization.
- Explore case studies of successful bioenergy projects and their impact on local communities and the environment.
By studying these key aspects of bioenergy, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of its role in the transition towards a more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy system.
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Fourth Grade. Electricity and magnetism
Study Guide Electricity and magnetism
Electricity and magnetism  Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson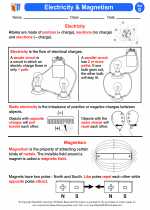 Electricity & Magnetism
Electricity & Magnetism  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Electricity and magnetism
Electricity and magnetism  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Electricity and magnetism
Electricity and magnetism  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Electricity and magnetism
Electricity and magnetism  Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key Electricity and Magnetism
Electricity and Magnetism  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Electricity and magnetism
Electricity and magnetism  Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key Electricity and magnetism
Electricity and magnetism 

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key

The resources above cover the following skills:
PHYSICAL SCIENCE
Energy
Plan and carry out investigations that explain transference of energy from place to place by sound, light, heat, and electric currents.
Demonstrate that electric circuits require a complete loop through which an electric current can pass.
Design, construct, and test a device that changes energy from one form to another (e.g., electric circuits converting electrical energy into motion, light, or sound energy; a passive solar heater converting light energy into heat energy).