Magnetic Field
A magnetic field is a region around a magnetic material or a moving electric charge within which the force of magnetism acts. This force is exerted on other magnets, magnetic materials, or moving charges.
Magnetic Field Lines
Magnetic field lines are used to represent the strength and direction of a magnetic field. They are drawn from the north pole to the south pole outside the magnet and from the south pole to the north pole inside the magnet. The density of the lines indicates the strength of the magnetic field, with the lines being more closely spaced where the field is stronger.
Properties of Magnetic Fields
Here are some key properties of magnetic fields:
- Direction: The direction of the magnetic field is from the north pole to the south pole outside the magnet and from the south pole to the north pole inside the magnet.
- Strength: The strength of the magnetic field is determined by the density of the magnetic field lines.
- Interaction with Other Objects: Magnetic fields exert forces on other magnets and magnetic materials. They also exert forces on moving electric charges, which is the principle behind electric motors and generators.
- Inducing Electric Currents: Changing magnetic fields can induce electric currents in conductors, a phenomenon known as electromagnetic induction.
Applications of Magnetic Fields
Magnetic fields have numerous practical applications, including:
- Electric motors
- Generators
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in medicine
- Magnetic compasses for navigation
- Magnetic data storage (e.g., hard drives)
Study Guide
When studying magnetic fields, you should focus on understanding the following concepts:
- The nature of magnetic field lines and how they represent the strength and direction of the magnetic field.
- The properties of magnetic fields, including their direction, strength, and interactions with other objects.
- The practical applications of magnetic fields in everyday devices and technologies.
- The relationship between magnetic fields and electric currents, including the concept of electromagnetic induction.
Additionally, it's important to practice using the right-hand rule to determine the direction of the magnetic field around a current-carrying wire or a straight conductor.
Remember to review examples and solve problems related to magnetic fields to reinforce your understanding of the topic.
Good luck with your studies!
.◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Fourth Grade. Electricity and magnetism

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson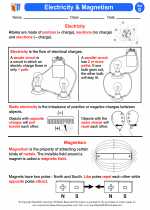
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
