Seasons
Seasons are the four main divisions of the year - spring, summer, autumn (fall), and winter - that are characterized by specific weather patterns and daylight hours. The changing of the seasons is caused by the tilt of the Earth's axis as it orbits the sun.
Causes of Seasons
The Earth's axis is tilted at an angle of approximately 23.5 degrees. This tilt causes different parts of the Earth to receive varying amounts of sunlight at different times of the year. When a particular hemisphere is tilted toward the sun, it experiences summer, while the opposite hemisphere experiences winter. As the Earth continues its orbit, the tilt causes the seasons to change.
Effects of Seasons
Each season brings specific changes in weather, temperature, and daylight hours. For example, summer is generally characterized by longer days, warmer temperatures, and more direct sunlight, while winter has shorter days, colder temperatures, and less direct sunlight. Spring and autumn fall in between, with mild temperatures and changing daylight hours.
Study Guide
- What causes the changing of the seasons?
- Describe the specific characteristics of each season.
- How does the tilt of the Earth's axis contribute to the occurrence of seasons?
- Explain why different parts of the Earth experience different seasons at the same time.
- What are the effects of seasons on weather, temperature, and daylight hours?
◂Science Worksheets and Study Guides Fourth Grade. Food webs/food chains

 Activity Lesson
Activity Lesson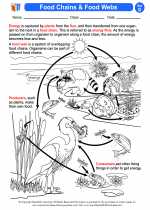
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Worksheet/Answer key
Worksheet/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
 Vocabulary/Answer key
Vocabulary/Answer key
